Everything You Need to Know About Critical Success Factors
Forward-thinking organizations understand that project success goes beyond meeting short-term deliverables. A successful project should also help an organization advance toward its big-picture goals.
This is where understanding critical success factors is relevant. Critical success factors are goals that bridge the gap between smaller project objectives and the long-term strategic goals of an organization.
When members of an organization understand what those critical success factors are, they can choose specific project success criteria that align with the business strategy. This, in turn, enables the organization to achieve meaningful results in line with its mission.
This article will go over everything you need to know about implementing critical success factors into your strategic planning.
What’s a critical success factor in project management?
Simply put, critical success factors (CSFs) are the goals your organization must achieve to reach strategic goals. Think of them as medium-level goals. They are longer term than project objectives, but more actionable than a strategic goal or the overall organizational mission.
If say, a strategic goal of an organization is to increase its market share in the healthy soft-drink space, then a critical success factor would be to increase consumer awareness of its products.
Once that success factor is defined, marketing campaigns and other actionable steps can be taken to achieve that success factor — which along with other CSFs (like improving the quality of the drinks) should help lead to the ultimate goal of increasing market share.
Benefits of defining and monitoring your critical success factors

Organizations can derive a multitude of benefits from clearly defining critical success factors. When critical success factors are incorporated into decision-making, you can expect the following benefits:
- Enhanced focus and direction: Defining critical success factors helps managers know what to prioritize, preventing effort from being directed toward activities that don’t align with priorities.
- Better stakeholder alignment: In organizations with many teams and large groups of stakeholders, having a common definition of success helps everyone row in the same direction.
- Simplified decision-making: Critical success factors allow for more consistency in decision-making. Since those factors are top-of-mind, each decision can be more deliberate and aligned with business priorities.
It may come as a surprise that 90% of organizations fail to reach their strategic goals. In large part, that’s because many organizations don’t detail what success looks like or how they will act to reach those goals. Despite that staggering number, only 51% of organizations create aligned goals and only 6% of those that do regularly revisit those goals.
Four key categories of critical success factors
Every organization and project operates with a unique set of circumstances. Inherently, this will shape what critical success factors look like. Recognizing this, we can still categorize critical success factors into four main categories:
Strategic critical success factors
These are high-level success factors that tie into your organization’s big-picture goals. Strategic critical success factors ensure your projects align with the broad objectives of your business.
If your company, for example, aims to become a leading provider of renewable energy, a strategic success factor could be improving renewable energy technologies. Based on this strategic success factor, the organization can encourage managers to prioritize innovation-driven projects.
Related: The Ins and Outs of the Strategic Planning Process
Temporal critical success factors
Temporal factors are the time-related success factors of a project. They can relate to the timing of deliverables or phases of a project. For example, launching a new consumer product in time for the holiday shopping season can be a temporal critical success factor.
Different areas of the project, from production, marketing, and execution would need to align with this important selling period for the project to succeed.
Industry critical success factors
These factors are the norms, trends, and competitive landscape of the industry in which your organization operates. An industry critical success factor might be to stay ahead of industry standards.
Think of a highly regulated industry like healthcare or a fast-evolving one like tech. In each context respectively, critical success factors might look like implementing compliance with new regulations or adopting the latest engineering best practices to maintain competitiveness.
Environmental critical success factors
Environmental critical success factors are the external elements that need to be worked around to reach your strategic goals. These can range from navigating economic conditions to changing consumer preferences.
Environmental success factors aren’t fully within your control but still require anticipation and contingency planning. The success of a construction project, for example, might depend on environmental success factors like obtaining permits from the government on time and the stability of local labor markets.
While the construction company cannot fully control each, they can take steps like working with an experienced consulting firm to file the paperwork and setting the project start date at a point where there is typically more seasonal labor available.
5 critical success factors commonly used in project management

In a project management context, critical success factors are the conditions a project manager needs to reach for a project to run smoothly. Unlike project success criteria, which refer to the specific goals a project team needs to achieve for a project to succeed, project success factors are more about what the project manager needs to accomplish for the project to run efficiently.
Here are five examples of project management critical success factors:
Proper project documentation
Documentation is never the most glamorous part of project management, but undoubtedly, it’s one of the most crucial. Proper project documentation ensures that all project details are recorded, decisions are traceable, and everyone involved has access to the same information.
Documentation can include project plans, progress reports, risk registers, and communication plans.
Executive involvement
Buy-in from leadership is a critical success factor that makes or breaks projects. Active support from executives ensures that projects can clear obstacles and receive the necessary resources on time. Plus, when project teams know they have support from leadership, they can take initiative and act with full confidence.
Encouraging engagement from leadership is therefore an important success factor for project managers.
Risk assessment
Controlling risk is another important element that project managers need to achieve for project success. A thorough risk assessment involves the project manager evaluating the likelihood of various risks and their potential impact on the project.
Once risks are identified, the project team can develop mitigation strategies and contingency plans. This can be done using a risk register document.
Communication protocols
Establishing a clear communication plan keeps important information moving seamlessly among team members and stakeholders. It’s an important critical success factor for projects since it's required for issue resolution, coordination, and keeping team members engaged with the project.
For a project manager, this means facilitating regular updates, scheduling time for feedback, and establishing procedures for addressing problems.
Stakeholder involvement
Finally, keeping all stakeholders involved is key. This means engaging with all the parties that have a vested interest in the project.
Inviting this input fosters buy-in and provides insights — while also reducing potential resistance. In a project that involves bringing a new product to market, for example, successfully engaging with stakeholders could involve inviting feedback on the product launch from upper management, the project team, suppliers, the eventual retailers, and the target audience.
How to choose critical success factors when initiating a new project

The previous section discussed critical success factors used by project managers at the project level. What’s useful about critical success factors is that they can also be set at the departmental and organizational levels.
When used in the latter contexts, critical success factors can help senior leaders determine what a project needs to accomplish to deliver value to the organization, or even whether the project is worth undertaking in the first place.
A leader can take the following steps to help projects achieve critical success factors:
Determine if the project aligns with your strategy
Consider whether the project aligns with the organization’s overarching strategy. If, for example, an organizational aim is to be more innovative than competitors, a critical success factor could be to develop new products every year. Based on this, leaders should evaluate projects based on whether they facilitate new, innovative products.
This evaluation ensures that initiatives are not siloed, irrelevant pursuits. Instead, they’ll be connected to the larger innovative mission of that organization.
Seek stakeholder feedback and build consensus
After you’ve determined that the project is aligned with strategy, reach out to key stakeholders. This includes the teams that will work on the project, company leadership, and potential end-users of the project.
Gather insights about their priorities and expectations. Garner their feedback on the critical success factors that you have outlined. After this exercise, you should have a clearer picture of whether a project should go forward or if it is misaligned.
Analyze risks and the external environment
Take a broad view of the external factors that could impact your project.
This involves considering market trends, regulatory changes, and the competitive landscape. Frameworks like the PESTEL analysis (Political, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal) guarantee that you’ve considered each of these factors and the ways they may impact your project.
Once a careful analysis is completed, the team should understand whether the project can successfully overcome its environmental success factors. Plus, if the team gets ahead of an environmental risk that can’t be solved, it prevents infeasible projects from going ahead at the expense of resources and time.
Set metrics for the critical success factors
After critical success factors are identified, the next logical step is to establish key performance indicators (KPIs) for these factors. These are the actionable metrics that will prove that success factors are met. This will give the team executing on the ground a clear idea of what they must accomplish for the project to succeed.
Monitor success factors with project management software
When you’re finally ready to turn your critical success goals into action, having the tools to monitor them goes a long way. Remember, only 6% of companies regularly revisit their goals. Project management software, like Rodeo Drive, takes much of the legwork out of tracking goal progress.
With a robust timeline-view planner to follow project phases and objectives, financial tools to keep projects on budget, and in-depth reporting — Rodeo Drive empowers project-based teams to stay on the right course.
Here’s how the platform works:
Activity planning and capacity management
The calendar-view planner enables project managers to visualize project timelines and assign activities to team members. Using the planner, teams can align their work with project timelines and set realistic goals when juggling multiple projects.
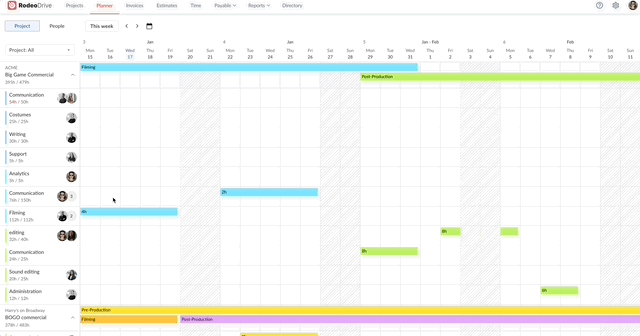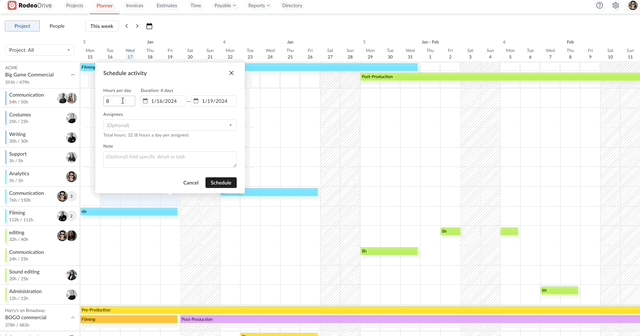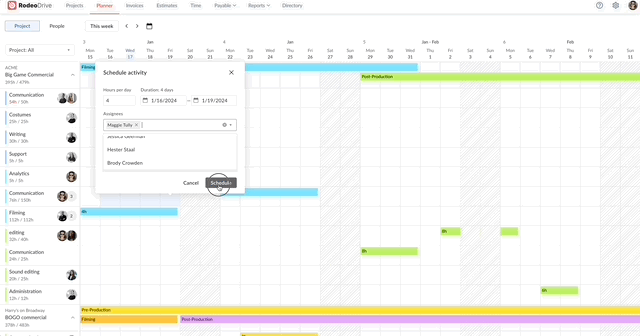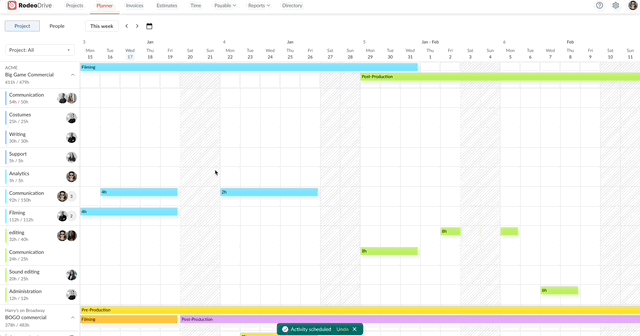
Assign team activities with Rodeo Drive’s intuitive timeline planner
Along with the timeline view, Rodeo Drive also features a people-view planner, designed to keep workloads balanced. The people view allows you to see how many project hours each team member has scheduled each day.
A green check mark indicates that a team member already has all of their available hours allocated to activities, whereas a red number shows that the team member has been overallocated.
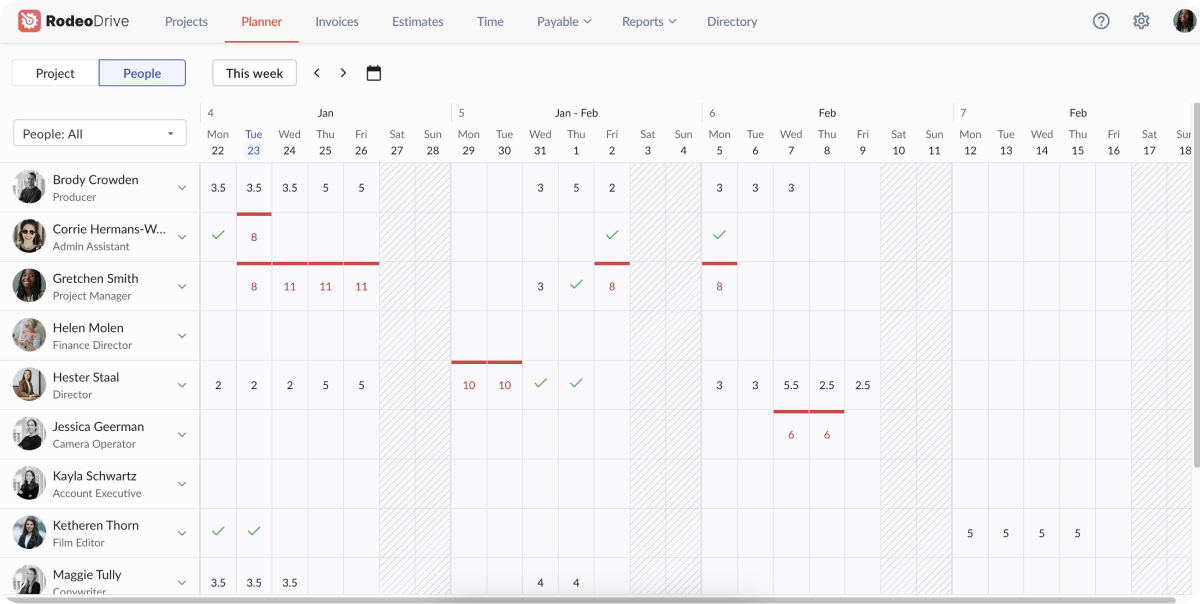
Manage workloads and find available capacity with the people-view planner
With the people planner, teams can stay ahead of burnout, find available capacity when needed, and sustainably pursue their long-term goals.
High-level project reporting
Rodeo Drive’s project reporting allows project managers to monitor the team’s progress alongside the financial health of all their ongoing projects. This includes three reports: projects, productivity, and time.
Within the Projects report, you can oversee project expenses and gross margins. This allows project teams to maintain a real-time, 360-view of profitability across projects, and stay within reach of their financial goals.
Additionally, the Productivity and Time reports give project managers an instant understanding of where team members are spending their time. This provides the insight necessary to make adjustments if time allocations aren’t aligned with priorities.
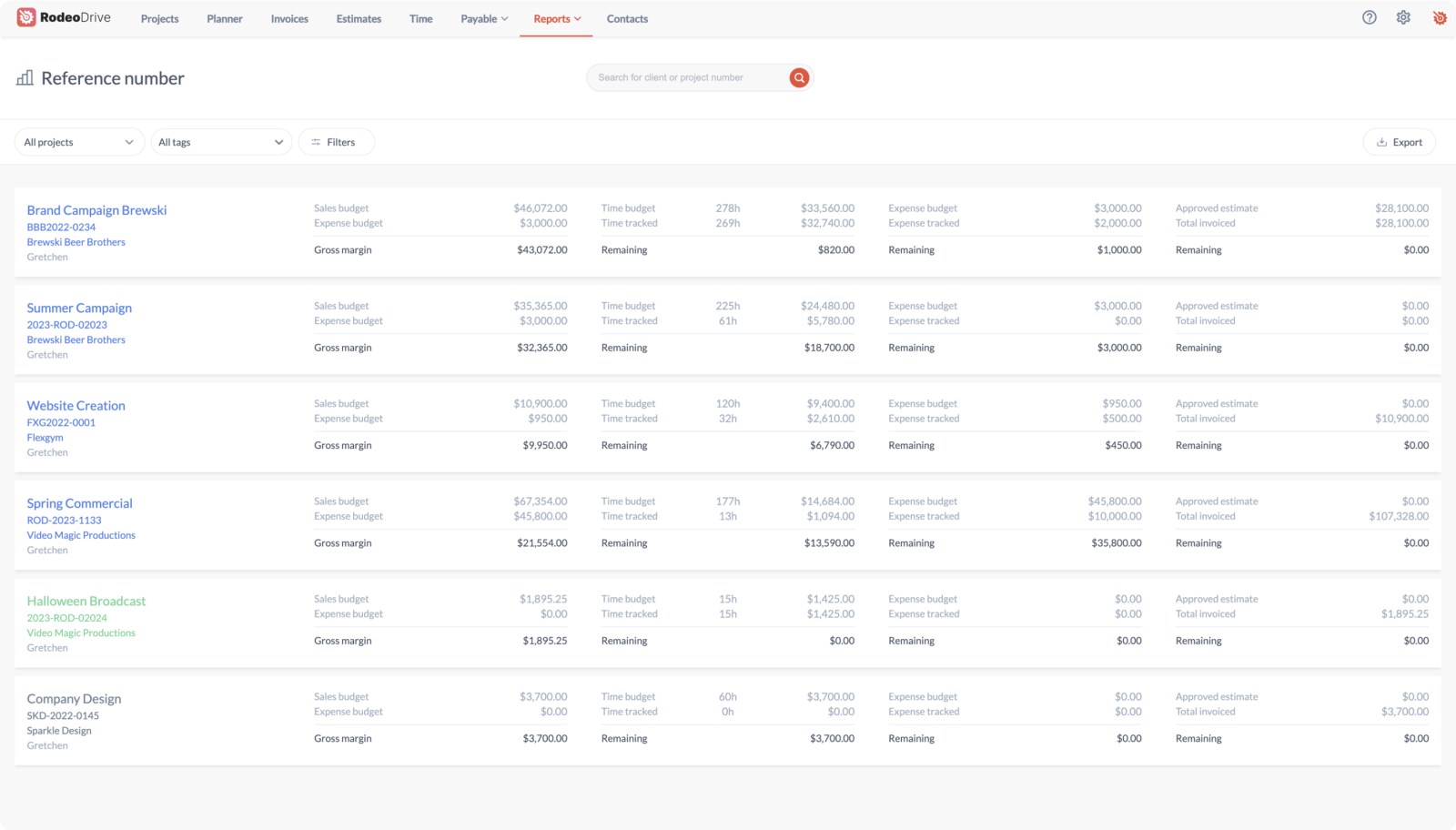
Oversee your profit margins and your remaining budget in the Projects report
The best part is you can use Rodeo Drive for free — no credit card needed. Some teams have even used it to achieve 30% greater project profitability. There’s no reason you can’t be next.
Try Rodeo Drive for free Schedule a demo
Critical success factors vs. key performance indicators
Key performance indicators and critical success factors have some important distinctions. Critical success factors are more qualitative, and based on your organization’s mission and strategic objectives. KPIs are quantitative and used to measure qualitative objectives like critical success factors.
Once you've established your critical success factors, you can then define relevant KPIs to monitor your performance in addressing each factor.
For example, if one of your critical success factors is "ensuring high customer satisfaction," your KPI could be "achieving a customer satisfaction score of at least 85%."
By following these steps, you can ensure that your project focuses on the right areas, aligns with broader organizational goals, and is positioned for success.
Key terminology for measuring project success
.png)
Along with KPIs, here are some additional terms that are related to, but distinct from critical success factors:
Project success criteria (CSC)
Project success criteria are the specific outcomes that must be met to consider a project successful. If critical success factors are the areas an organization needs to focus on, project success criteria are the benchmarks that determine whether a project has successfully addressed them.
For example, if one of your critical success factors is "effective stakeholder communication," a corresponding project success criterion could be "receiving positive feedback from at least 90% of stakeholders on communication effectiveness."
Key success area (KSA)
Key success areas are broad categories that are relevant to an organization’s success. Key success areas can include several crucial success factors. If customer satisfaction is an important part of an organization’s success, then there might be several related crucial success factors that address product quality, customer service, and user experience.
Key result area (KRA)
Key result areas, much like KSAs, are critical areas where satisfactory results will ensure the organization's successful performance. KRAs are often used in performance reporting to evaluate employee contributions to important business areas.
Additional examples of critical success factors
To bring these concepts to life, let’s explore some real-world examples of CSFs across different industries and projects:
- Software engineering project: A critical success factor might be "maintaining agile development practices," ensuring that the team can quickly adapt to changes and feedback throughout the development process. The corresponding success criteria could involve completing all scheduled sprints on time, with stakeholder feedback indicating high satisfaction with the iterative outputs.
- Construction project: For a construction project, a critical success factor could be "ensuring safety compliance," which is critical for the well-being of workers and the project's legal compliance. A measurable project success criterion here might be achieving zero safety incidents or violations throughout the project duration.
- Marketing campaign: In launching a new marketing campaign, a critical success factor could be "achieving target audience engagement." This might involve KPIs like reaching a certain number of impressions, clicks, or a specific engagement rate on social media platforms.
- Non-profit initiative: For a non-profit aiming to increase community awareness about a social issue, a critical success factor might be "community engagement and education." The success criteria could be measured by the number of community events held, attendance rates, and feedback surveys indicating increased awareness.
These examples underscore the importance of tailoring your critical success factors and project goals to the specific context of your business. Doing so ensures that project success translates into achieving the broader goals of your organization.








