A Complete Guide to Project Controls in 2024
As you probably know by now, projects very rarely go perfectly according to plan. Roadblocks, scope changes, and staffing changes will inevitably leave you scrambling to keep your project on track at some point during the project life cycle.
If this sounds familiar, implementing project controls might be something you’ll want to consider. Project controls help you quickly pinpoint issues that are hurting your project progress and swiftly correct them – and they eliminate some of your usual project chaos in the process.
In this blog, we’ll give you the rundown on everything you need to know about project controls, how they differ from project management, and the 5 components of controls you should be familiar with. Let’s get started.
What are project controls?
Project controls are processes that help keep projects on track from a cost and schedule perspective. The goal of implementing project controls is to eliminate the performance gap that often arises between project plan and execution.
The belief behind project controls is that a project’s budget and timeline are key determinants of project success and require detailed monitoring and data analysis.
Project controllers use project data to monitor the project’s timeline and spending, and should issues arise, project managers use their findings and recommendations to course correct and get the project back on track.
Project controllers are constantly looking at how the project manager’s planned progress compares to where the project is at and where it’s heading. In other words, project controllers compare project baselines to the project’s actuals and forecasts.
The idea is that with project controls, you can quickly catch issues that are causing your project to veer off track before they completely derail the project and cause it to fail altogether.
As we’ll dive into later on, implementing project controls involves having controls in place for each part of your project plan, which typically includes things like scheduling, risk management, and change management.
Having controls in place helps you better prepare for the unexpected.
Project Controls vs. Project Management
Although the two terms sound similar and have overlapping purposes, project controls are just one part of project management that is used to help project managers keep projects on schedule and under budget.
In a nutshell, project management manages 6 different constraints: Cost, Risk, Time, Quality, Scope, and Resources. Meanwhile, project controls are a subset of project management because they only involve overseeing the Cost and Time constraints.
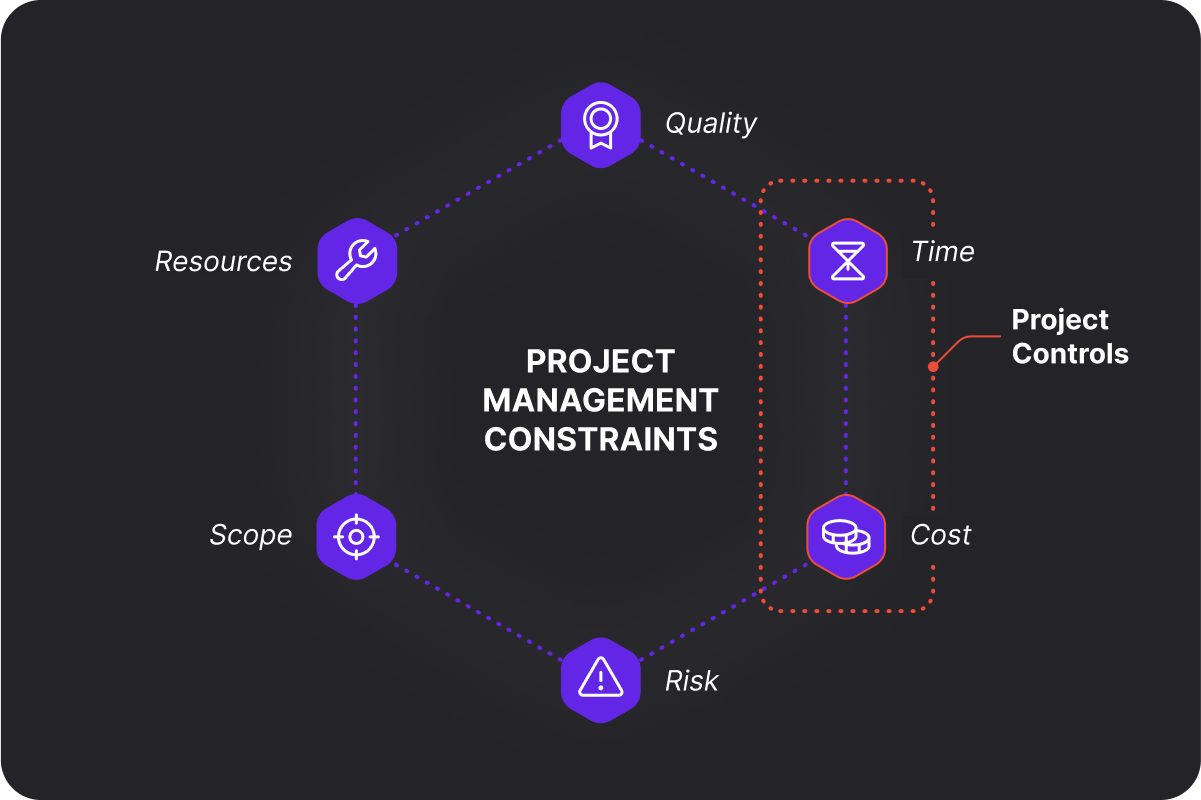
As such, project management has a much larger scope than project controls. It involves keeping the entire project on track, whereas project controls are mainly focused on analyzing data to deliver the project faster and cheaper.
Both concepts do work together though, as the project controls team uses data to help the project team with their objective of delivering the best possible project outcomes.
Manage your projects with Rodeo Drive
Project Controller vs. Project Manager
Project managers lead their project team through the project’s lifecycle, from initial planning to presenting the final deliverables. Their responsibilities typically include creating the project plan, assigning tasks, and ensuring all work is of high quality.
This means project managers are tasked with wearing several hats – they serve as the team manager but also liaise with the client and stakeholders to ensure everyone is on the same page. Should scope creep become an issue, they must determine how the team will deal with it.
Also read: The 26 Key Project Management Skills for Project Success
Conversely, the project controller position is an advisor to the project manager who tracks the progress of ongoing projects by collecting data and analyzing that data to both anticipate and solve problems.
If a project is far behind schedule or overspending beyond its budget, the project controller will consult the project manager on how to best course correct to move the project forward.
Although project controller and project manager are distinct roles, it’s not uncommon for a project manager to take on the project controller’s responsibilities rather than having a team member specifically responsible for project controls, particularly on a small team.
At the end of the day though, the project manager is the one responsible for ensuring projects are delivered on time, so they retain ultimate authority over which project controller recommendations to implement and which to ignore.
The 5 components of project controls and how to implement them
Introducing project controls into your workflows might feel intimidating at first. Breaking it down into these 5 components can make the implementation process easier:
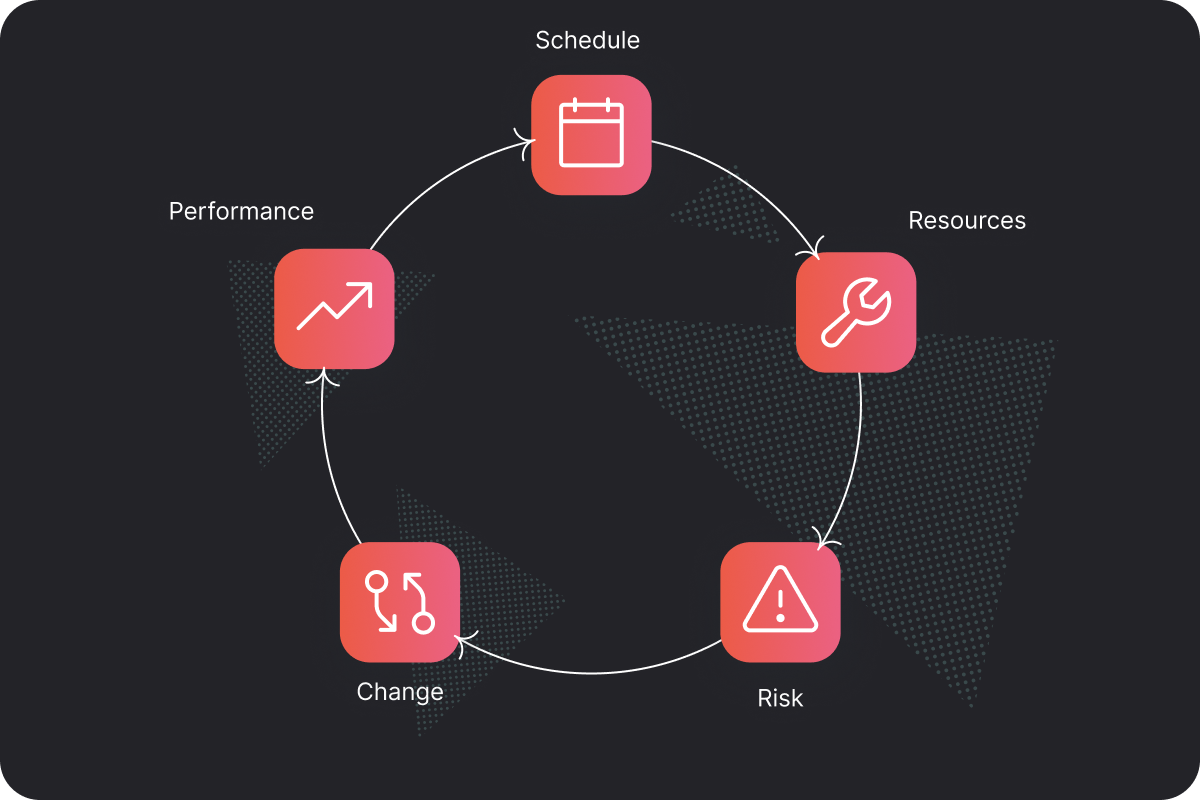
1. Schedule
Scheduling plays an important role in project controls, as you won’t be able to stick to a timeline if your schedule of tasks and resource allocation isn’t clearly defined from the get-go.
You’ll want to start your schedule by outlining the tasks required to complete the project and writing down the time requirements of each task. This will provide you with an accurate structure that you can use to create your timeline.
Visual tools – such as Gantt charts – are another great resource to help with scheduling that can help you better visualize the sequence of your timeline and each phase of the project.
2. Resources
Project resources include everything from money to time to materials. Mismanaging any of these resources can cause a project to fail, which is why this is such an important part of project controls.
Resource management begins with establishing exactly what resources are at your disposal before the project kick-off. For example, if the client has a hard deadline for the deliverables, then it’s critical to know that your time and resource is limited while you’re creating your project schedule.
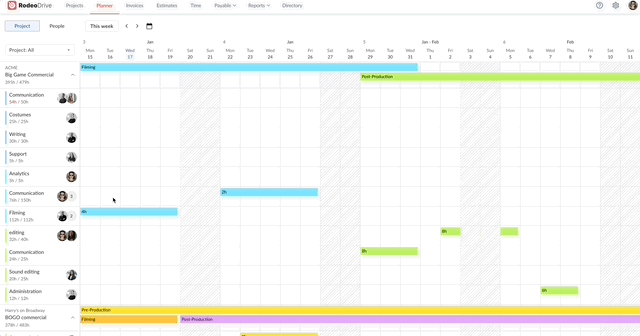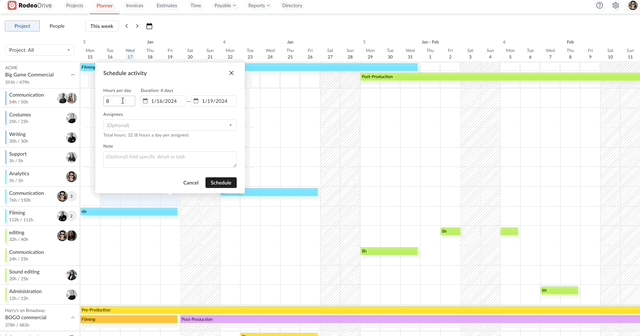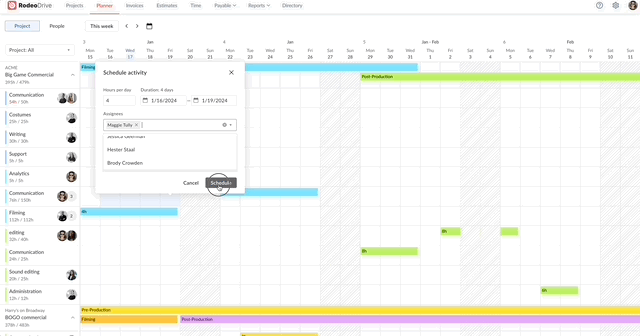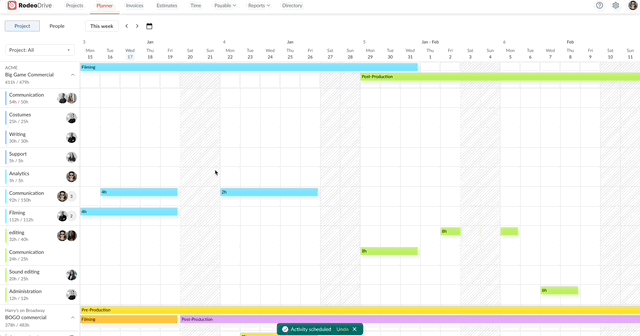
Your access to resources might inevitably change during the project, which is why it’s critical to exercise proactive resource management and be prepared to quickly find a solution, should an unforeseen delay occur. Project controls help you do so.
3. Risk
The whole idea of project controls is to identify and mitigate risks to the project’s timeline and costs and remedy them as soon as they occur.
The key to effective risk management is to create a thoughtful risk register – also known as a risk management plan – that identifies risks to your project, assesses the likelihood of each, how to mitigate them, and assigns them to a team member to monitor.
Creating this type of document will help you be better prepared in the event that any of these risks occur. Any part of your project may involve risks, but project controls are specifically focused on risks involving timeline and budget.
4. Change
Seasoned project managers are likely already familiar with the importance of change management. Oftentimes, projects undergo sudden timeline, staffing, or scope creep changes that impact the overall project schedule and allocation of resources.
An example of scope creep could be when the client drastically changes the requirements for the deliverables in a way that impacts the team’s timeline or the contents of their work.
Preparing a change management plan and outlining a change control process ahead of time can create a formalized process that allows stakeholders and project managers to review and accept or decline proposed changes.
5. Performance
It’s difficult to know whether your project is on track for success if you’re not monitoring your project team’s performance along the way. There are numerous ways you can track project performance, including milestones met, billable hours recorded, or on-time completion of assigned tasks.
Establishing Key Performance Indicators, OKRs, and SMART goals are other ways to monitor performance and ensure all team members are working toward clearly defined goals.
Many project management software tools also include reporting features that can serve as a resource for insights on employee-specific and teamwide performance.
Popular project control methods
Project managers looking to implement project controls without a dedicated project controller’s help will be relieved to know that you can do so using traditional project management techniques that you’re likely already familiar with.
Any process that helps measure and track the 5 components outlined above is considered a method of project control. Here’s a look at 4 techniques you can get started with:
Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed (RACI) Matrix
A RACI Matrix is a diagram that defines the responsibilities of each team member and plots those responsibilities against the project’s major tasks.
These matrices are known to eliminate role confusion and clarify where team members should focus their attention – both of which can be beneficial in keeping a project schedule on track.
From a project control perspective, RACI matrices can significantly improve resource allocation. This is because they prevent time resources from being overallocated to one task and under-allocated to another. It also ensures that all tasks are accounted for and that none slip through the cracks during the scheduling process.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A work breakdown structure is a method that adopts a deliverable-oriented approach to planning projects. In essence, you can create a WBS by looking at your overall deliverables and breaking them into smaller pieces. From there, you identify the tasks necessary to complete the smaller pieces of the puzzle.
In working backward from the final deliverables, you’re left with a complete list of tasks needed to effectively deliver on the project objectives. Doing so will make it easier to plan your project timeline.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
The critical path method is a way of determining the minimum time required to complete a project based on a visual map of task sequences.
To do so, you’ll need to create a list of all project tasks and their dependencies – which you can also do by creating a WBS. The critical path method takes things one step further than WBS though, as you’ll need to then write down an estimate of how long you expect each task to take.
Once you’ve done so, your longest sequence of critical project tasks can be identified as your critical path, which is what establishes your entire project timeline. The idea is that your critical path sets the pace of the entire project, so you must prevent delays on this path in order to avoid derailing your entire project timeline.
Project Charter
A project charter is different than the other methods on this list, as it’s less of a method and more of a detailed planning document. Your project charter should define your goals and objectives, project scope, and necessary resources in detail, as you will likely need to refer back to it throughout the project.
Project charters can be considered a method of project control because they also outline project risks and how those risks will be monitored and mitigated during the project as well as details on how project resources will be allocated.
Having a centralized place for this critical information helps implement project controls. A project charter template can help you get started.
Related: Project Administration: A Crucial Part of Project Management
How and when to use project controls
You’ll want to implement project controls at the very beginning of your project’s lifecycle to ensure that you never lose control of your timeline and budget. That said, project controls should exist for the entire duration of your project.
The good news is, several project control methods – such as project charters and work breakdown structures – are designed to be implemented at the beginning anyway.
It’s important to note that project controls are iterative processes that must be revisited throughout the project. So even if you’ve used certain methods like CPM or WBS, there will likely be certain points in the project life cycle where your controls require extra attention.
For example, if you’re noticing that your project performance is not meeting expectations, you should evaluate and address the issue by taking the following steps:
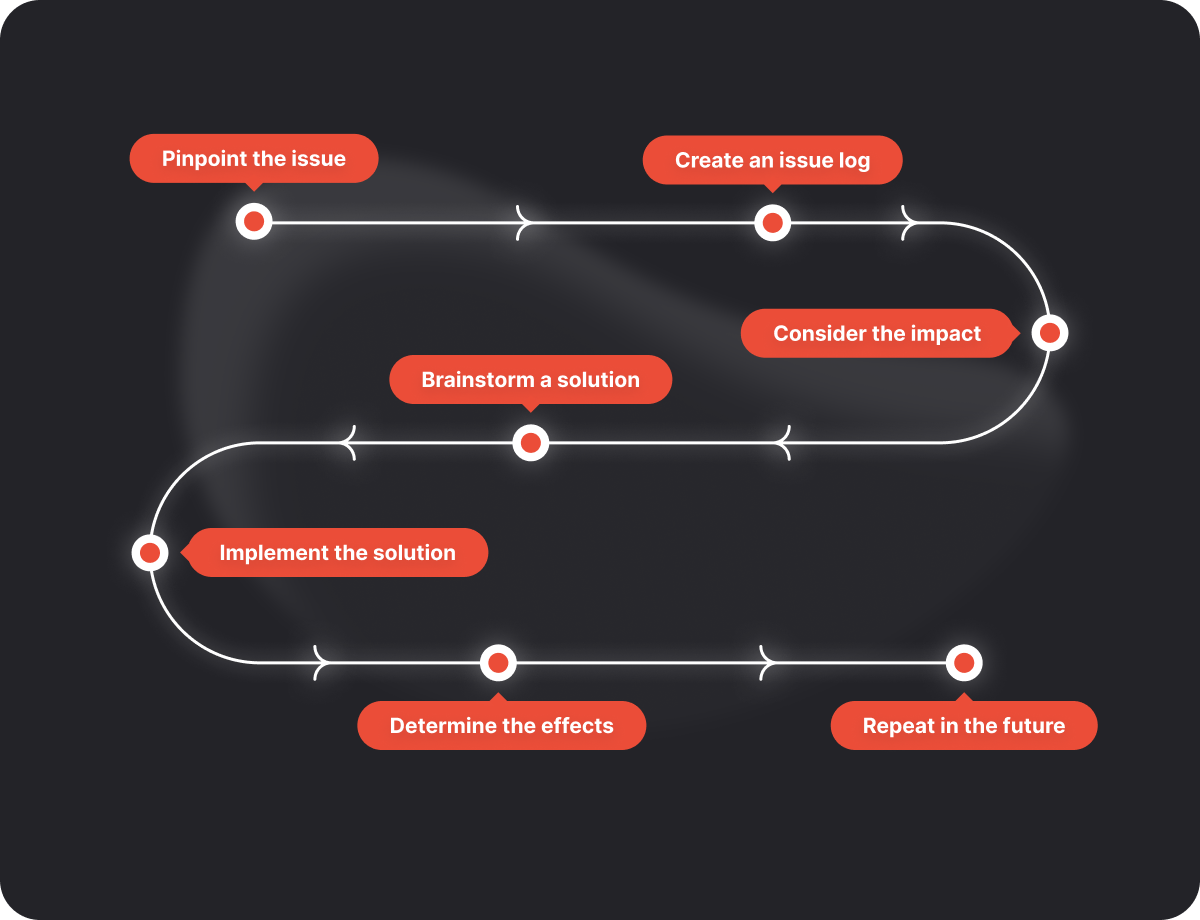
- Pinpoint the issue that’s causing a lack of performance.
- Create an issue log.
- Consider how the issue is impacting your cost and timeline.
- Brainstorm a solution.
- Implement your solution to correct the issue.
- Determine if the solution was effective by monitoring the situation.
- Repeat for future issues.
Following these steps, in addition to implementing more formalized project control methods, will ensure that your team is equipped to overcome all possible roadblocks and still deliver your project deliverables on time and within budget.
Related: The Project Management Checklist: 12 Steps to Follow
Optimize project controls with Rodeo Drive
As we’ve discussed, scheduling and cost management are at the heart of project control. In order to monitor these two constraints effectively, you’ll want to enlist the help of a project management tool.
Rodeo Drive is an all-in-one project management software solution that can help you do so without the need to rely on third-party integrations. Those looking to add project controls to their work will especially benefit from the following features:
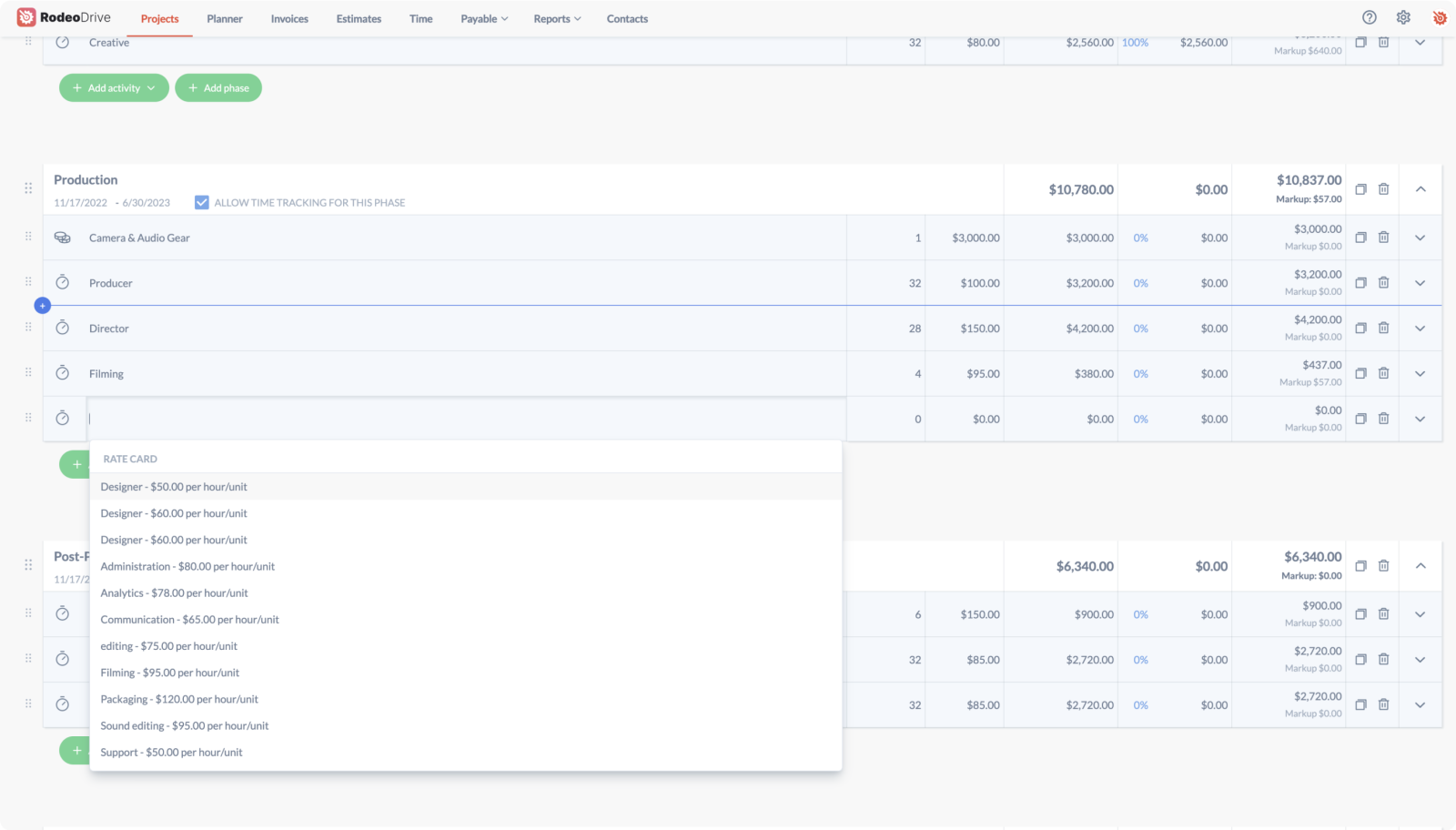
Detailed phase-based budgeting
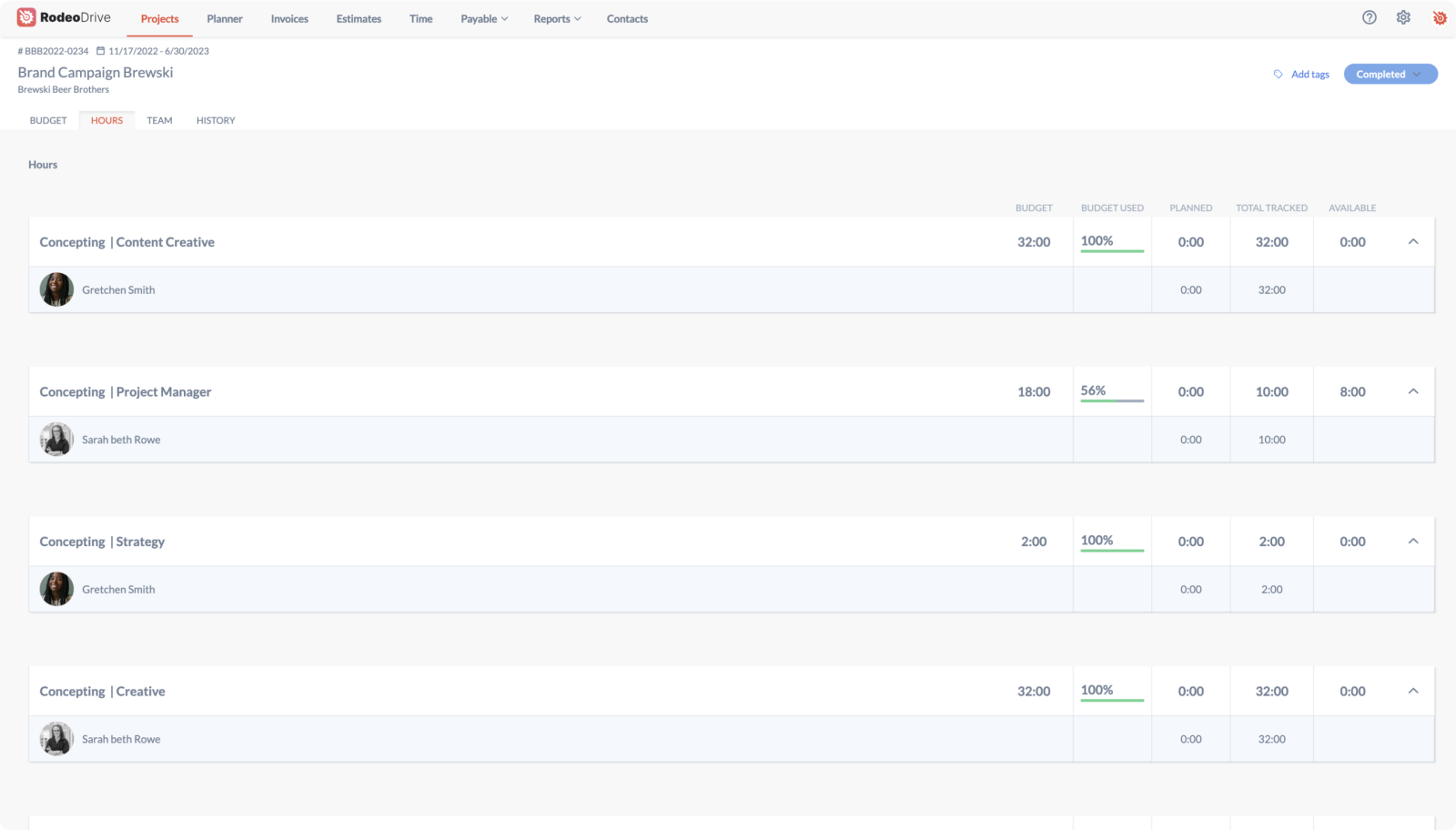
All projects begin with building a budget in Rodeo Drive, which helps you get a handle on your project finances right at the very beginning. Rodeo Drive's budgeting feature is broken down into phases, with time and budget requirements included in each phase.
Building budgets in this way makes it easier for project managers to identify what specific activities have caused the team to overspend, as Rodeo Drive updates in real time to show how much of your budget has been spent as you work on the project.
Easy-to-use time tracking that’s interconnected with your budget
There are two ways to track time in Rodeo Drive – either start the stopwatch via the planner when you begin a task or add a timecard later if you forget. All of your features are connected in Rodeo Drive, meaning when you track time toward a task, your budget will automatically update to account for the value of your time.
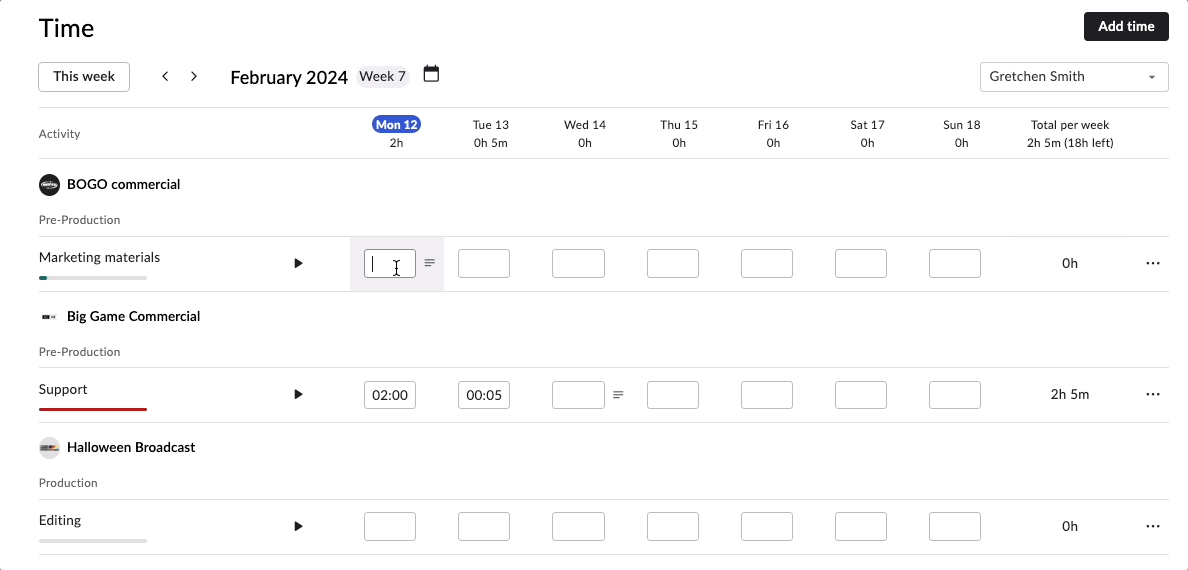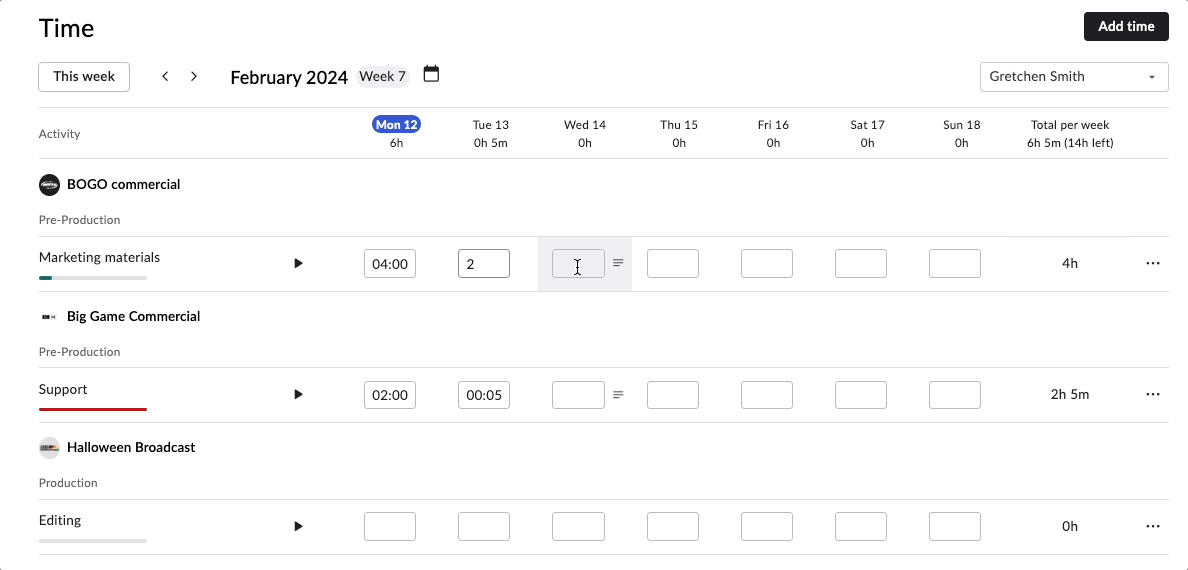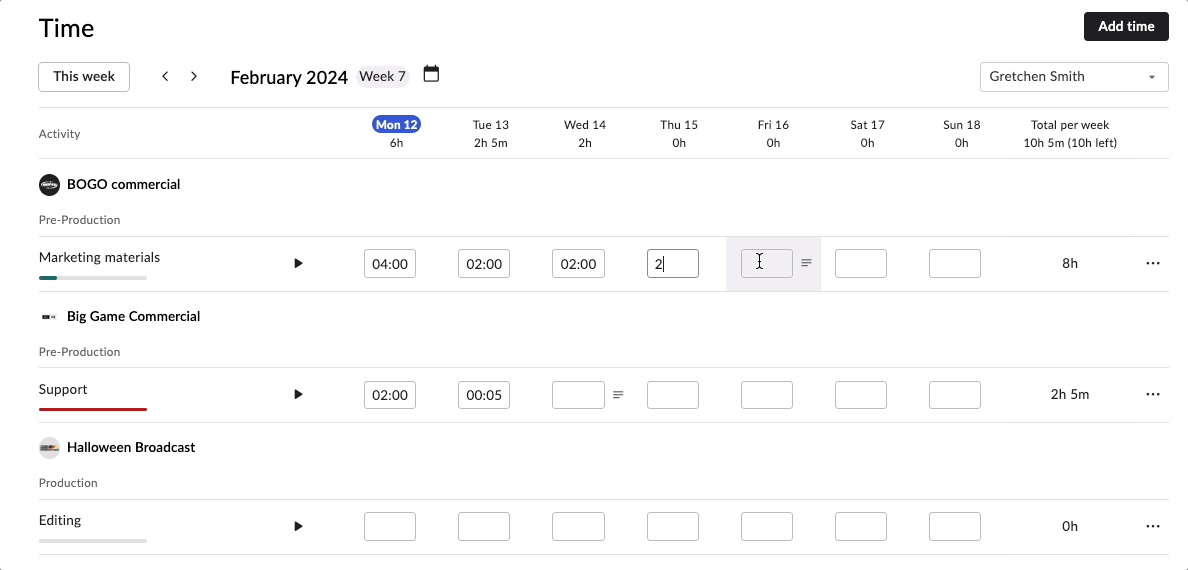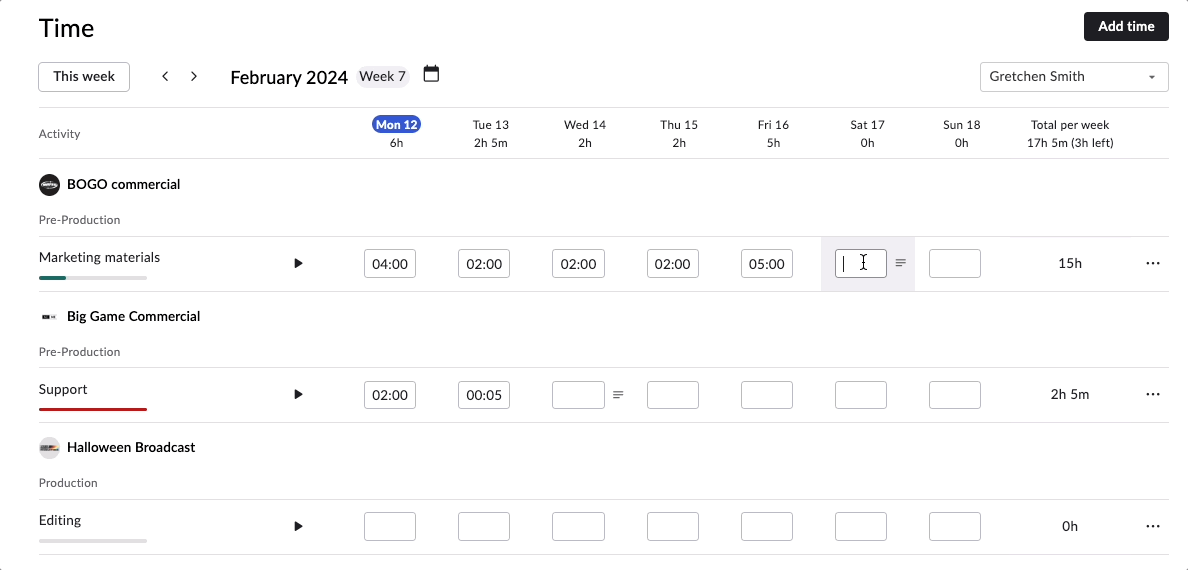
From a project control perspective, this will help you identify roadblocks that are causing your team to waste valuable time and, in turn, derail your budget.
Say, for example, your team is struggling to finalize the storyboard for a commercial they’re working on. You’ll be able to visualize and identify that delay through Rodeo Drive, as the number of hours they’re spending on that task will be higher than the number of hours you budgeted for it.
Reports with data-driven insights into time registration and project progress
Without data, it’s nearly impossible to properly oversee your project controls. Luckily, Rodeo Drive provides reports based on productivity, financial project data and time registration.
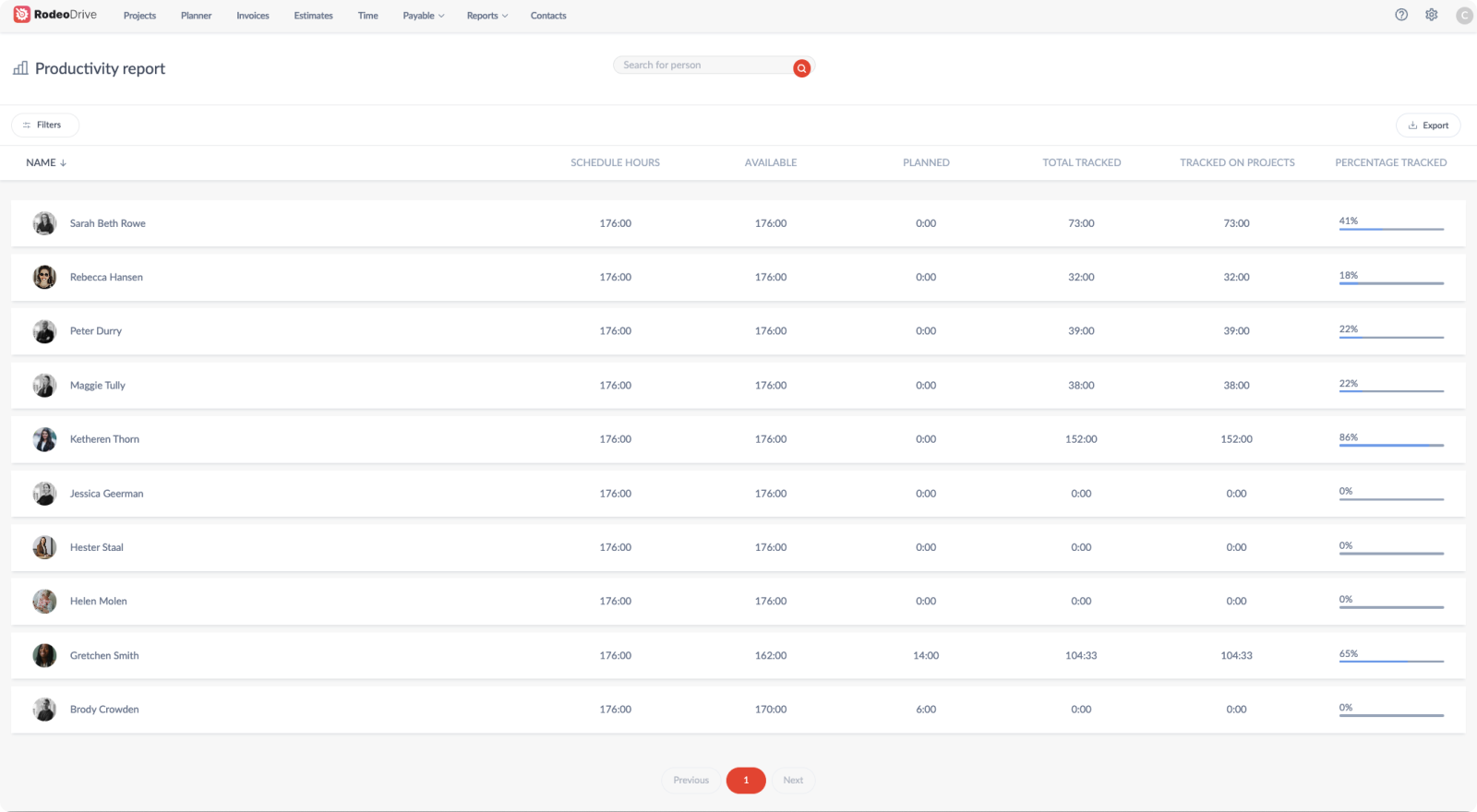
These will provide you with several metrics ranging from the profitability of your projects to the number of billable hours your team is recording – and which clients they’re billing the most. Knowing how your budget estimates correlate to your actuals is enormously helpful in planning future projects, as you’ll know how to build even more accurate estimates next time.
Additional features:
- Estimating: Send an estimate to your client for approval – straight from the platform.
- Invoicing: Send customizable invoices to clients based on the time you’ve logged into Rodeo Drive.
- Expense tracking: Keep track of your project expenses and purchase orders all in one place.
- Integration with QuickBooks (US) and Xero (UK): To help with bookkeeping.
Looking for a tool to help you implement project controls? Try out Rodeo Drive for free today.








